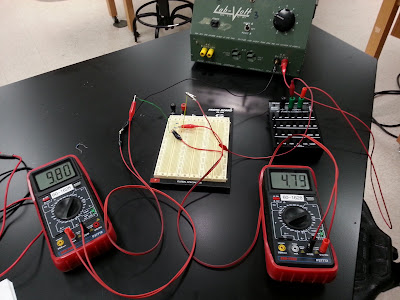
Our setup consisted of a resistor box as the shunt resistor and the three parallel load resistors at 1000 Ω each, wired to the breadboard, all connected in series. An ammeter was connected in series with the system to measure IBUS and a voltmeter is connected parallel to the load resistors to measure VBUS.
Our data goes as follows:
1 Load
Req = 9.79 Ω
VBUS = 5.49 V
IBUS = 5.65 mA
PLoad
2 Loads
Req = 489 Ω
VBUS = 4.75 V
IBUS = 9.80 mA
PLoad
3 Loads
Req = 326 Ω
VBUS = 4.25 V
IBUS = 13.19 mA
PLoad
PLoad can be calculated as
PLoad = IBUS2 Req
By adding a fourth 1 kΩ resistor parallel to the circuit, and assuming the shunt resistance and voltage supply remains the same, the new load voltage was calculated to be 5.525 V.
If we wanted to reduce the load voltage variation to ±1% for the 3-load case, our source parameters would have to be VS = 5.05 V and RS = 46.2 Ω.
No comments:
Post a Comment